Table of Contents
A useful and space-saving way for visitors to access a variety of options, dropdown menus are an essential component of web design. This thorough tutorial will cover the principles of dropdown menus, their significance in web design, and how to improve their usability and appearance using CSS pseudo-elements::before and ::after.
Understanding Dropdown Menus
Dropdown menus, sometimes referred to as drop-down menus, are interactive components that are frequently seen in user interfaces. Usually, they are made up of a parent element, such a button or link, that, when clicked, exposes a concealed list of options. These choices may consist of form choices, navigational links, or other interactive components.
Dropdown menus are versatile and can serve various purposes, including:
- Navigation
Dropdown menus are frequently used to arrange website navigation and make it easier for users to access various website areas. Their ability to offer a hierarchical framework makes browsing easier, especially on sites with a lot of content. - Form Inputs
Dropdown menus are commonly used in forms to give users with predefined options for selecting values, such as choosing a nation, selecting a product category, or selecting a date from a calendar. - Contextual Actions
Dropdown menus can be used in some applications to display context-specific options or actions associated with a single item or section. For instance, a dropdown menu may include choices for sharing, editing, and removing a particular item from a list.
Why Use Dropdown Menus?
Dropdown menus offer several advantages that make them a popular choice in web design:
- Space Efficiency
Dropdown menus save screen space by hiding items until they are required, making them perfect for websites with limited space or complex navigation structures. - Organizational Hierarchy
Designers can use dropdown menus to organize material hierarchically, allowing visitors to dig down into certain categories or sections without overwhelming them with too much information at once. - User Control
Users can customize their browsing experience with dropdown menus, which save up interface space while giving them access to more options and information when needed. - Consistency
Dropdown menus provide a consistent interface pattern that consumers are accustomed with, resulting in a more intuitive and predictable user experience across multiple websites and applications.
Enhancing Dropdowns with CSS Pseudo-elements
Output of examples :
While dropdown menus are a common feature in web design, their appearance and behavior can be improved with CSS pseudo-elements::after and::before. These sophisticated tools enable designers to alter dropdown menus without cluttering the HTML syntax, allowing for a variety of creative possibilities.
Let’s examine an example 1 : to see how CSS pseudo-elements can be used to create a Basic-level dropdown menu:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<link rel="preconnect" href="https://fonts.googleapis.com">
<link rel="preconnect" href="https://fonts.gstatic.com" crossorigin>
<link href="https://fonts.googleapis.com/css2?family=Montserrat:ital,wght@0,100..900;1,100..900&display=swap"
rel="stylesheet">
<style>
body {
font-family: "Montserrat", sans-serif;
font-optical-sizing: auto;
font-style: normal;
}
.dropdown {
position: relative;
/* Make the dropdown container the reference point */
width: 200px;
display: inline-block;
}
.dropdown-toggle {
padding: 20px 15px;
border: none;
background-color: #008CBA;
cursor: pointer;
width: 100%;
color: white;
font-size: 16px;
font-weight: 400;
}
.dropdown-menu {
display: none;
/* Hide the menu initially */
position: absolute;
left: 0;
background-color: #ffffff;
list-style: none;
padding: 0;
width: 100%;
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
box-shadow: 0px 8px 16px 0px rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.2);
z-index: 1;
}
.dropdown-menu li {
display: block;
}
.dropdown-menu li a {
color: black;
padding: 12px 16px;
text-decoration: none;
display: block;
font-size: 14px;
}
/* Change color of dropdown links on hover */
.dropdown-menu li a:hover {
background-color: #f1f1f1
}
.dropdown:hover .dropdown-menu {
/* Show the menu on hover */
display: block;
}
/* Dropdown arrow using ::after */
.dropdown-toggle:after {
content: "";
position: absolute;
top: 50%;
right: 10px;
transform: translateY(-50%);
/* Center the arrow vertically */
border-style: solid;
border-color: #ffffff transparent transparent transparent;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="dropdown">
<button class="dropdown-toggle">Select an Option</button>
<ul class="dropdown-menu">
<li><a href="#">Option 1</a></li>
<li><a href="#">Option 2</a></li>
<li><a href="#">Option 3</a></li>
</ul>
</div>
</body>
</html>In this example, we have a Basic-level dropdown menu .
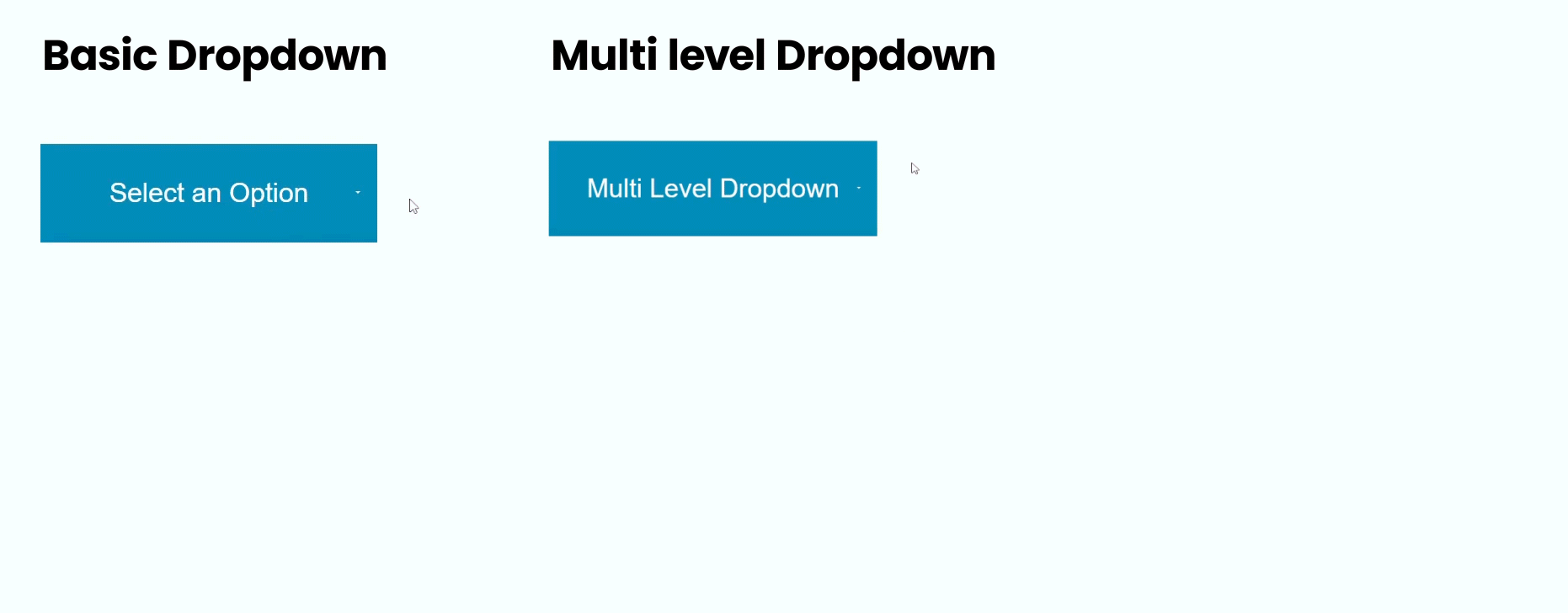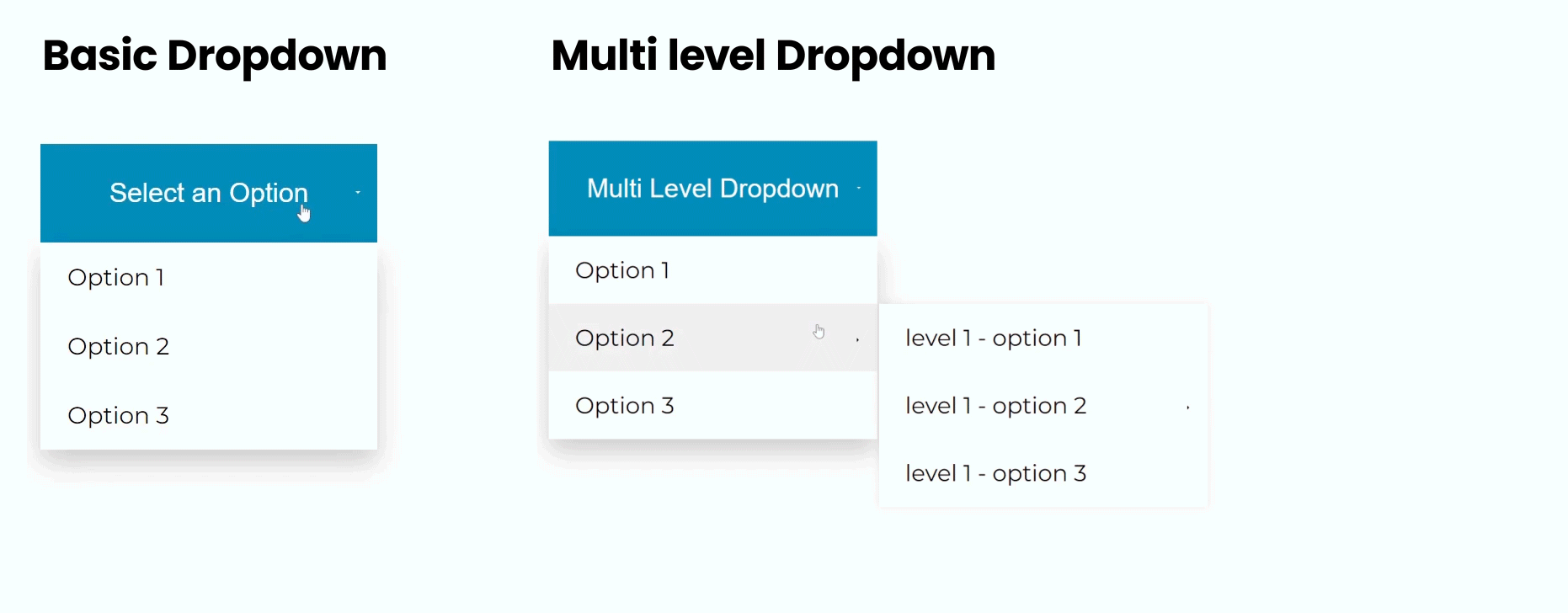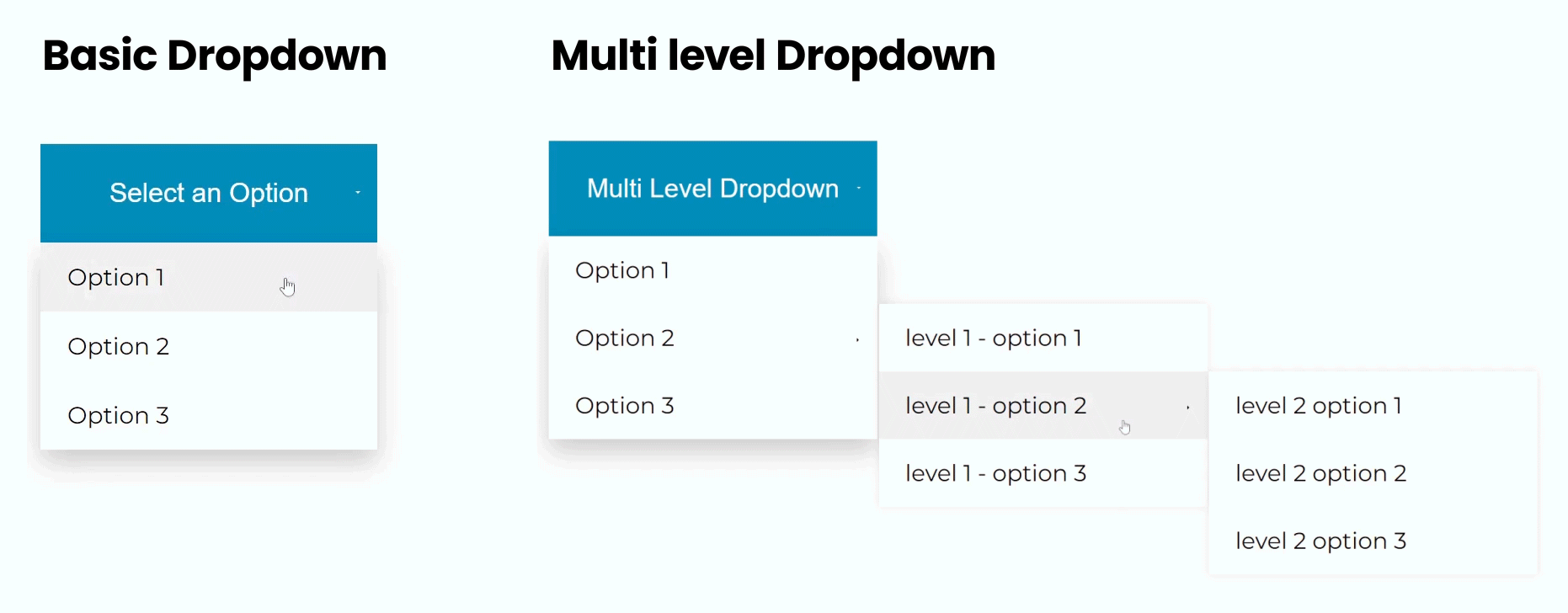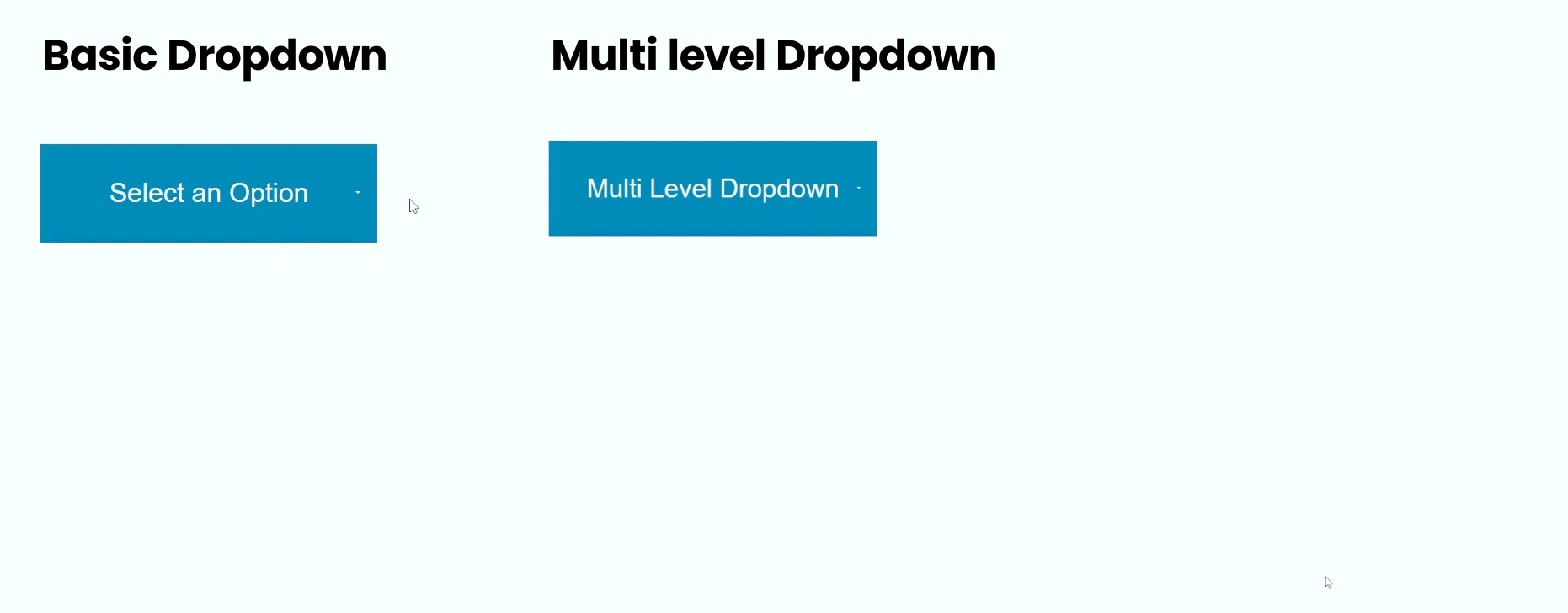
Let’s examine an example 2 : to see how CSS pseudo-elements can be used to create a multi-level dropdown menu:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<link rel="preconnect" href="https://fonts.googleapis.com">
<link rel="preconnect" href="https://fonts.gstatic.com" crossorigin>
<link href="https://fonts.googleapis.com/css2?family=Montserrat:ital,wght@0,100..900;1,100..900&display=swap"
rel="stylesheet">
<style>
body {
font-family: "Montserrat", sans-serif;
font-optical-sizing: auto;
font-style: normal;
}
.dropdown {
position: relative;
/* Make the dropdown container the reference point */
width: 200px;
display: inline-block;
}
.dropdown-toggle {
padding: 20px 15px;
border: none;
background-color: #008CBA;
cursor: pointer;
width: 100%;
color: white;
font-size: 16px;
font-weight: 400;
}
.dropdown-menu {
display: none;
/* Hide the menu initially */
position: absolute;
left: 0;
background-color: #ffffff;
list-style: none;
padding: 0;
width: 100%;
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
box-shadow: 0px 8px 16px 0px rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.2);
z-index: 1;
}
.dropdown-menu li {
display: block;
}
.dropdown-menu li a {
color: black;
padding: 12px 16px;
text-decoration: none;
display: block;
font-size: 14px;
}
/* Change color of dropdown links on hover */
.dropdown-menu li a:hover {
background-color: #f1f1f1
}
.dropdown:hover .dropdown-menu {
/* Show the menu on hover */
display: block;
}
/* Dropdown arrow using ::after */
.dropdown-toggle:after {
content: "";
position: absolute;
top: 50%;
right: 10px;
transform: translateY(-50%);
/* Center the arrow vertically */
border-style: solid;
border-color: #ffffff transparent transparent transparent;
}
/* -----------------------------level 1 ------------------- */
.has-level-1-submenu {
position: relative;
}
.has-level-1-submenu:hover .level-1-submenu {
display: block;
}
.has-level-1-submenu:after {
content: "";
position: absolute;
top: 50%;
right: 10px;
transform: rotateZ(270deg);
/* Center the arrow vertically */
border-style: solid;
border-color: #000000 transparent transparent transparent;
}
.level-1-submenu {
display: none;
position: absolute;
left: 201px;
width: 100%;
top: 0;
background-color: #ffffff;
list-style: none;
padding: 0;
width: 100%;
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
box-shadow: 0px 0px 5px 0px rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.1);
z-index: 1;
}
/* ------------level 2 same as level 1 ------------------------------- */
.has-level-2-submenu {
position: relative;
}
.has-level-2-submenu:hover .level-2-submenu {
display: block;
}
.has-level-2-submenu:after {
content: "";
position: absolute;
top: 50%;
right: 10px;
transform: rotateZ(270deg);
/* Center the arrow vertically */
border-style: solid;
border-color: #000000 transparent transparent transparent;
}
.level-2-submenu {
display: none;
position: absolute;
left: 201px;
width: 100%;
top: 0;
background-color: #ffffff;
list-style: none;
padding: 0;
width: 100%;
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
box-shadow: 0px 0px 5px 0px rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.1);
z-index: 1;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="dropdown">
<button class="dropdown-toggle">Multi Level Dropdown</button>
<ul class="dropdown-menu">
<li><a href="#">Option 1</a></li>
<li class="has-level-1-submenu">
<a href="#">Option 2</a>
<ul class="level-1-submenu">
<li><a href="#">level 1 - option 1</a></li>
<li class="has-level-2-submenu">
<a href="#">level 1 - option 2</a>
<ul class="level-2-submenu">
<li><a href="#">level 2 option 1</a></li>
<li><a href="#">level 2 option 2</a></li>
<li><a href="#">level 2 option 3</a></li>
</ul>
</li>
<li><a href="#">level 1 - option 3</a></li>
</ul>
</li>
<li><a href="#">Option 3</a></li>
</ul>
</div>
</body>
</html>In this example, we have a multi-level dropdown menu with nested submenus. Each submenu is styled using CSS classes to control its appearance and behavior.
Best Practices for Dropdown Design
When designing dropdown menus, it’s essential to follow best practices to ensure an optimal user experience:
- Clarity and Simplicity
Dropdown menus should be basic and intuitive, with fewer options and less crowded designs to avoid user confusion. Use clear labels and succinct writing to properly express menu alternatives. - Accessibility
Ensure that dropdown menus are accessible to all users, including those utilizing assistive technology such as screen readers or keyboard navigation. Use keyboard shortcuts, focus indicators, and descriptive labeling to make navigating easier for all users. - Responsive Design
Design dropdown menus that are flexible to different devices and screen sizes, adjusting their appearance and behavior as needed. Test menus on several devices to ensure a consistent and seamless user experience. - Performance Optimization
Optimize dropdown menus for performance by reducing the use of sophisticated CSS styles and animations, especially on mobile devices with limited memory. Prioritize speed and efficiency to improve the overall browsing experience.
Conclusion
Dropdown menus are an essential component of web design, providing users with a simple and fast method to explore webpages, enter data, and perform contextual actions. Using CSS pseudo-elements::after and::before, designers can improve the functionality and aesthetics of dropdown menus, resulting in visually appealing and user-friendly interfaces. Experiment with these strategies on your own projects to fully see the potential of dropdown menu design and improve your web design skills.
